Rotating Detonating engine
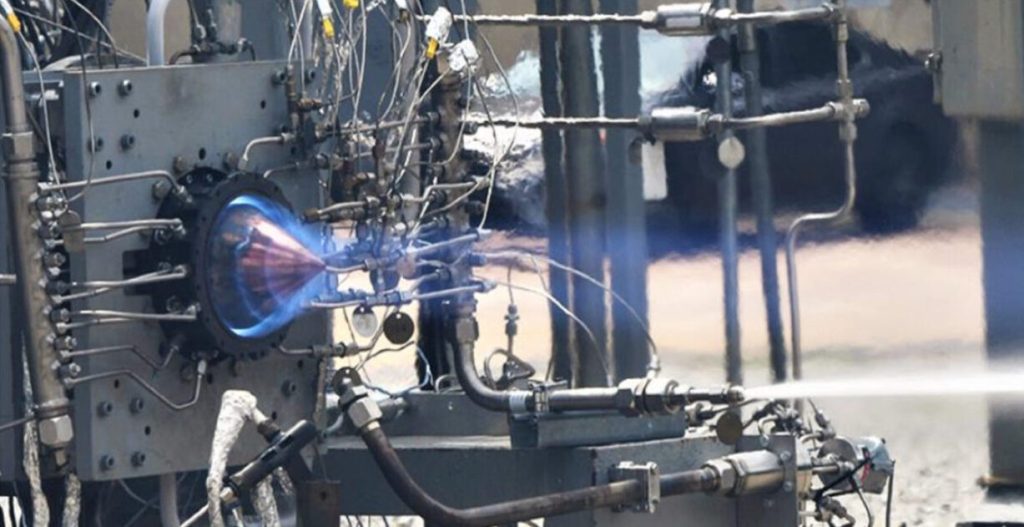
Imagine a revolutionary engine that harnesses the power of controlled explosions, not fiery blasts, to propel spacecraft. That’s the rotating detonation engine (RDE), a technology NASA is pioneering to fuel the future of space travel. Here’s the lowdown on this fascinating engine:
Concept:
Think of a circular racetrack where explosions zoom around constantly. That’s the basic RDE setup.
Fuel and oxidizer (like oxygen) enter the circular chamber, like race cars lining up at the starting grid.
A spark ignites the mixture at one point, triggering a detonation – a super-fast, supersonic explosion that travels around the ring like a lightning bolt.
As the detonation wave races around, it continuously ignites the unburned fuel and oxidizer ahead, keeping the party going.
Hot, high-pressure exhaust gasses blast out of the nozzle at the back, propelling the engine and any attached spacecraft forward.
Benefits:
Fuel efficiency: RDEs could be 25% more efficient than traditional rocket engines, requiring less fuel for the same thrust. Think of it as getting better gas mileage on your spaceship!
Simplicity: The design has fewer moving parts compared to complex rocket engines, making it potentially more reliable and easier to maintain.
Controllability: Engineers can fine-tune the fuel flow and detonation timing to adjust the engine’s thrust, ideal for delicate maneuvers like docking spacecraft.
Challenges:
Noise: Detonations are loud, creating concerns for missions near Earth or other sensitive environments.
Instability: Controlling the spinning detonation wave can be tricky, leading to potential engine vibrations and performance issues.
Development stage: RDEs are still under development, requiring more research and testing before they can blast off on real missions.
Applications:
Deep space exploration: RDEs could power spacecraft on long-haul journeys to distant planets and beyond.
Hypersonic vehicles: Their high thrust and controllability could make them ideal for super-fast Earth-to-orbit aircraft.
Reusable rockets: Their simpler design might make them easier to reuse for multiple launches, reducing the cost of space travel.
While RDEs face some hurdles, their potential is enormous. NASA is actively pushing the boundaries of this technology, and who knows, maybe one day these engines will be whispering through the cosmos, powering a new era of cleaner, more efficient space exploration!


