Air taxis have the potential to completely transform the way we travel through the skies. NASA is fully committed to turning this vision into a reality and is actively collaborating with industry partners to address one crucial aspect – reducing aircraft noise in our communities.
As we look towards the future, it becomes evident that quiet flight will play a pivotal role, especially when air taxis and drones take off and land in designated vertiports located in both rural and urban areas. These vertiports will seamlessly integrate into our communities, ensuring a smooth and efficient transportation system.
To support the industry in designing vehicles that prioritize noise reduction, NASA is equipping them with the necessary tools to predict noise levels during the vehicle’s design phase. By providing these tools well in advance, companies can make informed decisions and optimize their designs even before seeking certification from the Federal Aviation Administration.
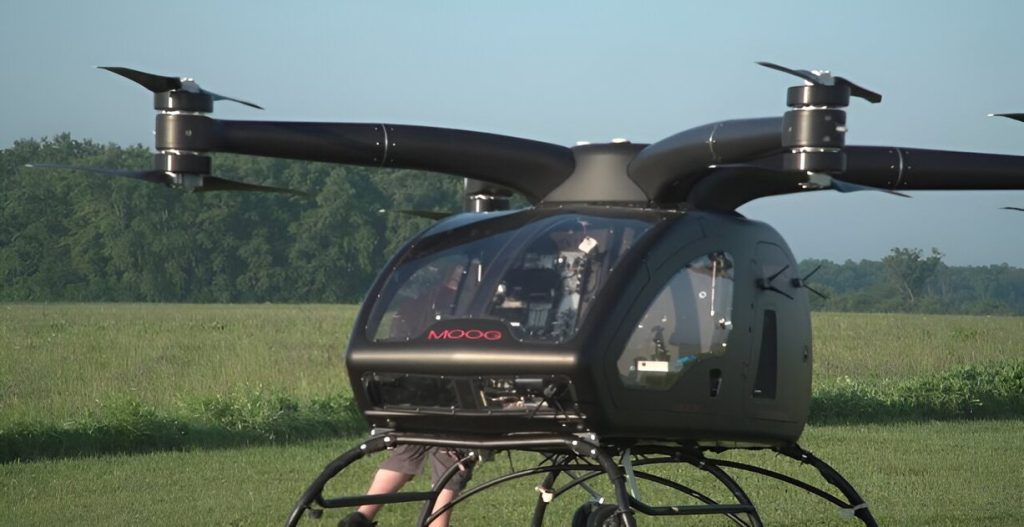
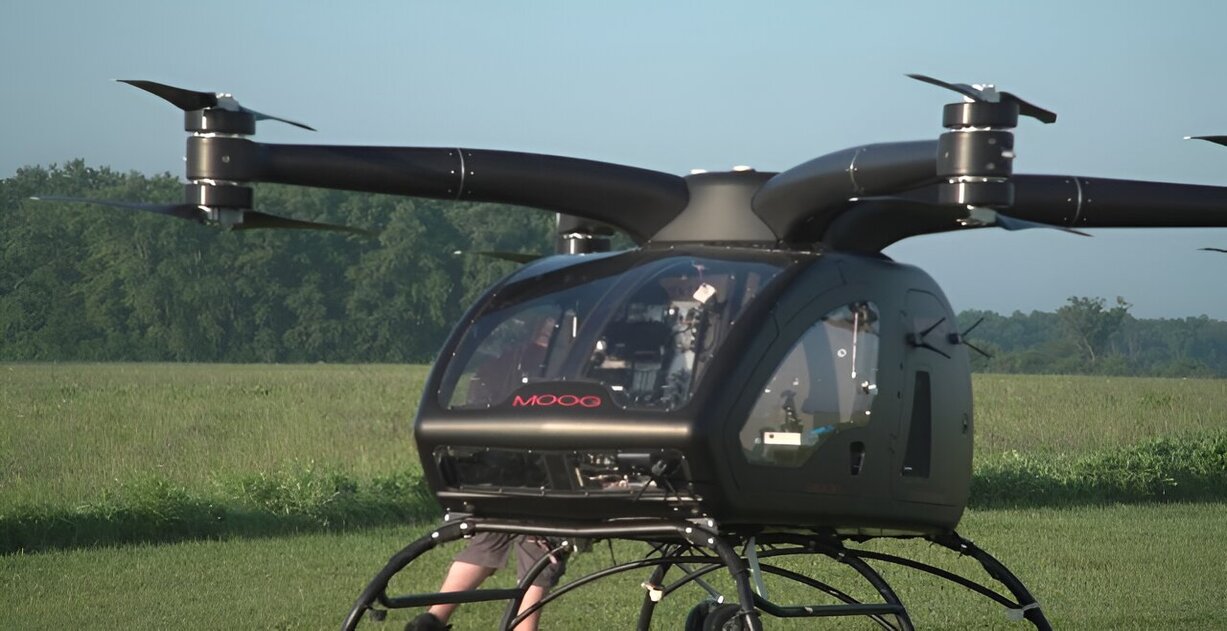
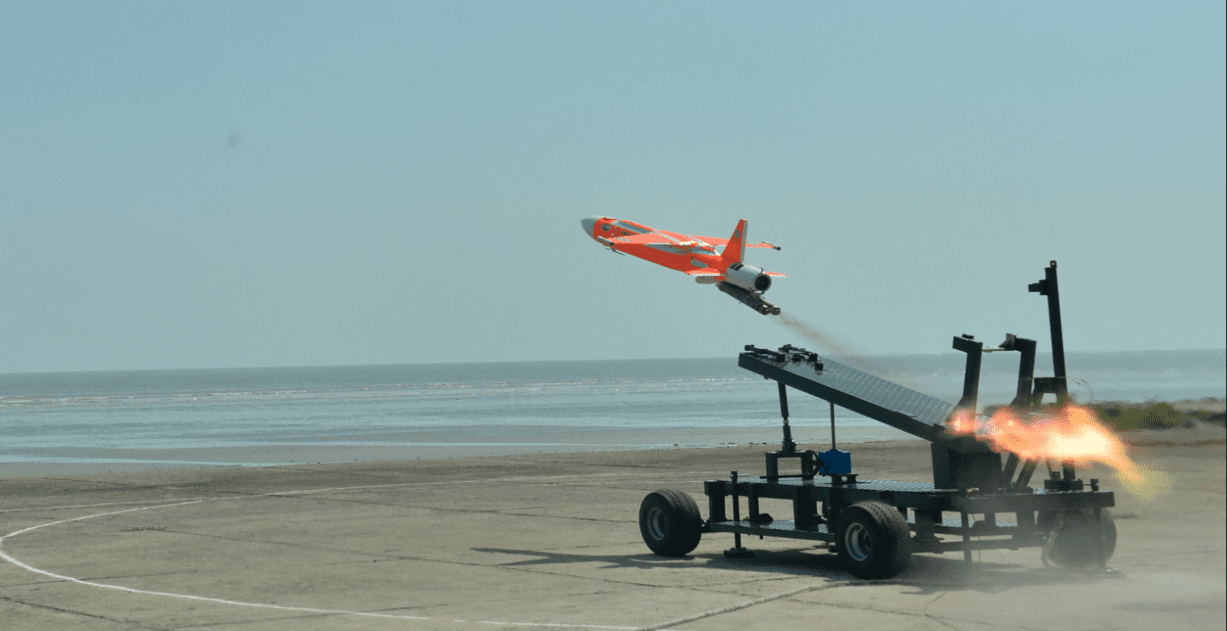
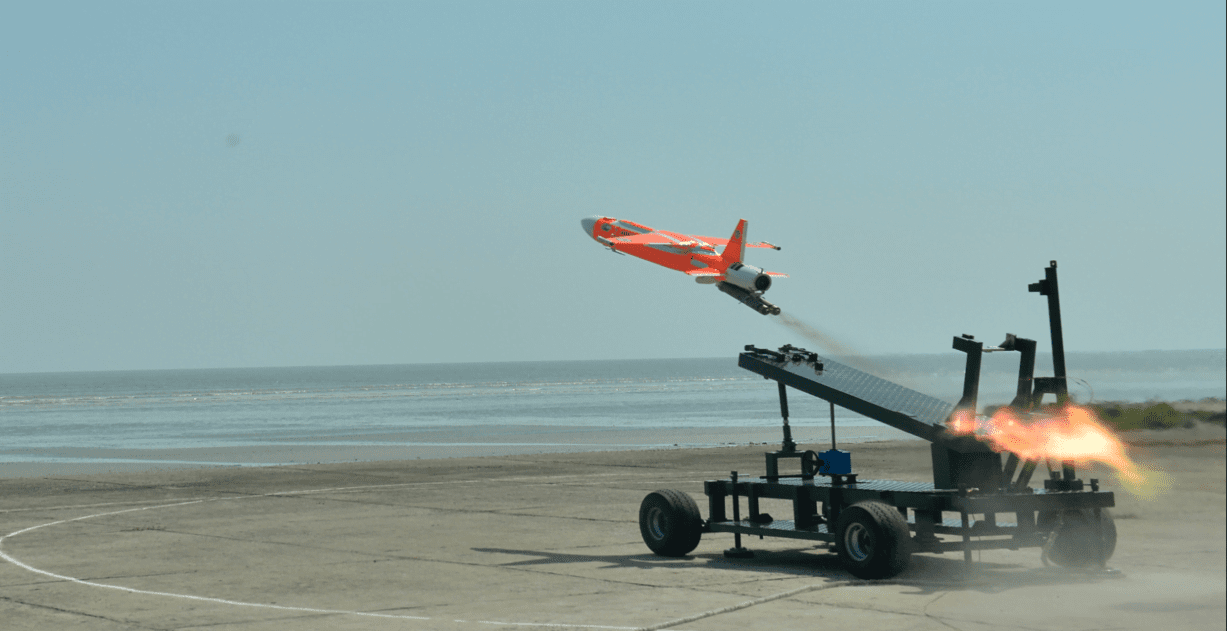
In a significant step towards this goal, NASA’s researchers from the Glenn Research Center traveled to the Springfield-Beckley Municipal Airport in Ohio during the summer of 2023. Their mission was to test an electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) taxi developed by Moog. Throughout the testing process, NASA’s team collected valuable data during the aircraft’s departure, landing, and even while it hovered at an altitude of 60 feet. The eVTOL was remotely piloted by a skilled operator from a nearby ground station.
This collaboration with Moog marked the second round of testing conducted by NASA. In 2022, researchers had already acquired noise data during the initial piloted testing phase, where the Moog vehicle hovered in a fixed location.
The data collected from both rounds of testing will be instrumental in enhancing and validating NASA’s noise prediction tools. The agency is committed to sharing these tools, along with the comprehensive dataset, with the U.S. industry. By doing so, NASA aims to assist in the design process of quiet air taxis and drones, ensuring that they meet the highest standards of noise reduction.
This groundbreaking research is being carried out under NASA’s Revolutionary Vertical Lift Technology (RVLT) project, which falls under the agency’s Advanced Air Vehicles Program. The RVLT project aligns with NASA’s Advanced Air Mobility Mission, which aims to provide the industry with crucial data to guide the development of electric air taxis and drones. Together, we are shaping the future of air transportation, making it quieter, more efficient, and accessible for all.